143|137|7||1672896601|7|1673035528|0| 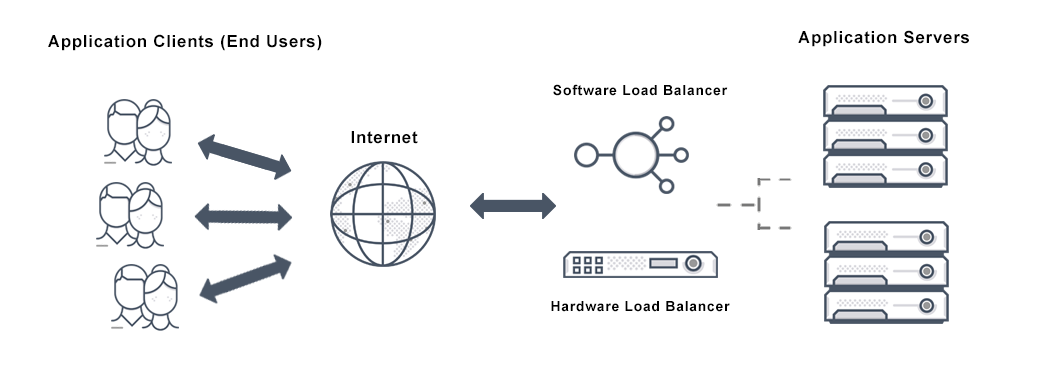
Web load balancing is the process of distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers or resources in order to improve the performance and availability of a website or web-based application.
Load balancing is often used in environments where a single server or resource is not able to handle the workload or traffic of a website or application, or where it is important to ensure that the website or application remains available even if one of the servers or resources fails.
There are several methods of load balancing, including:
1. Round-robin: In this method, incoming requests are distributed to servers in a predetermined order. For example, if there are three servers, the first request would go to the first server, the second request would go to the second server, the third request would go to the third server, and the fourth request would go back to the first server.
2. Least connections: In this method, incoming requests are distributed to the server with the fewest connections or lowest workload.
3. Least response time: In this method, incoming requests are distributed to the server with the fastest response time.
4. Weighted round-robin: In this method, servers are assigned a weight, and incoming requests are distributed based on the weight of the servers. For example, a server with a weight of 2 would receive twice as many requests as a server with a weight of 1.
Load balancing can be implemented in hardware, such as with a load balancer appliance, or in software, such as with a load balancer software program. It is often used in combination with other technologies, such as caching and compression, to improve the overall performance and scalability of a website or application.
In summary, web load balancing is the process of distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers or resources in order to improve the performance and availability of a website or web-based application. There are several methods of load balancing, including round-robin, least connections, least response time, and weighted round-robin. It can be implemented in hardware or software and is often used in combination with other technologies to improve performance and scalability.
Here is a brief overview of these concepts:
1. Web load balancing: Web load balancing is the process of distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers or resources in order to optimize the performance and availability of a website.
This can be done using hardware or software load balancers, which act as intermediaries between clients and servers and route traffic to the most appropriate resource.
Load balancers can improve the performance of a website by reducing the load on individual servers, increasing the capacity of the system, and improving the reliability of the website.
2. Caching: Caching is the process of storing data in a temporary location in order to reduce the number of times that data needs to be retrieved from its original source. Caching can improve the performance of a website by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transferred over the network and by reducing the load on the server.
There are various types of caching that can be used, including browser caching, server caching, and content delivery network (CDN) caching.
Web load balancing and caching are often used together to improve the performance and scalability of websites.
Load balancers can distribute traffic to servers that are optimized for caching, and caching can reduce the load on those servers by storing frequently accessed data in a temporary location.
By using these techniques, websites can handle more traffic and provide a better user experience.